
The concept of building energy conservation needs to be deeply rooted in the hearts of the people. It is very important to establish the implementation strategy of building energy conservation, and there must be specific measures and effective methods for the implementation of building energy conservation strategy.
The building energy efficiency regulations and specifications of German/i>
I Origin of building energy conservation specificatopn
The German specification for building energy conservation was published on November 16, 2001 and implemented on February 1, 2002. It is referred to as << The specification for building energy conservation 2002>> [13]. Its predecessor is the building insulation specification and building heating equipment specification. The earliest date can be traced back to the building energy conservation regulations of 1976. After that, the building energy conservation specification was revised every 2-3 years. The current version is specified for energy conservation of buildings 2012, and the next version is specification for energy conservation of buildings 2014.
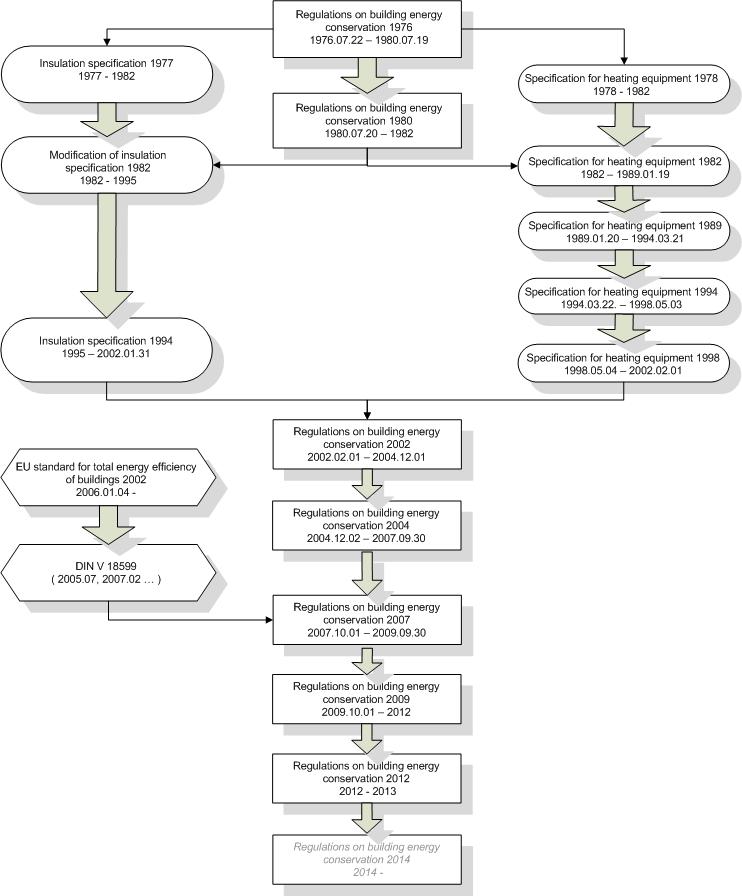
List of building energy efficiency specifications in Germany
II The main contents and application scopes in the building energy conservation specifications
The marker difference between the building energy efficiency specification and the previous specifications is that it stipulates that the existing buildings and new buildings should be gradually equipped with building energy consumption certificates. The certificate is used to mark and compare the energy-saving performance of buildings and to show when approving, building, selling or renting buildings.
Other main contents of the specification for building energy efficiency include the following aspects:
- The energy-saving requirements and calculation methods for new buildings;
- The energy-saving requirements and calculation methods for reconstruction, expansion and reconstruction buildings;
- The energy-saving requirements and calculation methods of building equipment, namely heating, air conditioning, ventilation and hot water supply equipment;
- Provisions on handling violations of specifications;
The building energy conservation specification of Germany excludes energy for production, but does not exclude buildings used for production, but for all buildings that use heating equipment in daily life (indoor general temperature above 19 ºC, outside 12 ºC, annual use of equipment for more than 4 months). The building energy conservation specification divides buildings into two types and treats them respectively according to different standards:
Residential buildings: housing, such as residential housing, nursing home, kindergarten, etc;
Non residential buildings: public buildings and other buildings, such as for office, commercial or finance, transportation or communication, science, education, culture, health and entertainment, factories, workshops, etc;
At present, China divides buildings into industrial buildings and civil buildings, and civil buildings are divided into residential buildings and public buildings. The implementation ignores industrial buildings and forgives civil buildings, focusing only on public buildings [12]. Therefore, the scope is not wide enough, and the awareness of building energy conservation has not been popularized by the whole people.
III Definition of building energy consumption in energy saving specification
Energy materials are divided into basic energy materials (or original ecological energy materials), secondary energy materials and final energy materials.
Original ecological energy refers to natural energy, such as oil, natural gas, coal, wood, atomic fuel, solar energy, wind energy, hydro energy, geothermal energy, etc. Among them, the first five are consumption type and the last four are renewable type.
Secondary energy materials are converted from original ecological energy materials, such as electricity, canned fuel oil, wood carbon, biochemical biogas, canned gas, etc. there will be energy loss in the conversion process. The secondary energy materials converted from renewable natural energy are called green energy, such as electric energy obtained by hydraulic or wind power, thermal energy obtained by geothermal energy, etc.
Final energy materials are the materials used for energy supply in buildings, such as electricity, fuel oil, coal, firewood, gas, heating, solar energy, etc. imported from heating manufacturers.
Some of the final energy materials are directly from the original ecological energy materials, and some are from the secondary energy materials.
The demand for original ecological energy in the specification refers to the demand for non renewable original ecological energy.
--- The energy conservation specification requires to calculate the total demand for final energy materials of buildings (Qe, unit: per square meter per year, kWh / m2 a):
The total demand for residential buildings is the sum of the final energy materials required for heating and hot water;
The total demand for nonresidential buildings is the total of the final energy materials required for heating, hot water, air condition and lighting;
This quantitative scale makes it possible to compare the energy-saving performance of buildings with different physical properties and different equipment.
--- The energy conservation specification requires to calculate the total demand for original ecological energy of buildings (Qp, unit: per square meter per year, kWh/m2a):
The demand of original ecological energy is based on the demand of final energy materials, considering the energy consumption required for the production, transportation, distribution and storage of final energy materials.
This quantitative scale not only makes the evaluation of building energy consumption more scientific, but also makes it possible to compare the resource damage and environmental pollution caused by building energy consumption and the effectiveness brought by the use of green energy.
--- The intermediate results of calculating the above demand, such as heating energy demand (QH), hot water energy demand (Qw), air conditioning energy demand (Qk), lighting energy demand (Ql), equipment energy loss (Qt), can be used to dissect and analyze the energy consumption performance of buildings and recommend and compare different energy-saving schemes;
Refer to the following schematic diagram for the influence factors and mutual relations considered in the calculation. The corresponding symbols are:
Qp: Original ecological energy demand( (calculation is required from the energy saving specification 2002)
Qe: Final energy demand;
fp: Conversion coefficient from final energy demand to original ecological energy demand;
QH: Energy required for heating;
QW: Energy required for hot water( (calculation is required from the energy saving specification 2002)
Ql: Energy required for lighting( (calculation shall be made for nonresidential buildings)
Qk: Energy required for air conditioning( (calculation shall be made for nonresidential buildings)
Qt: Energy lost by building heat conduction
Qv: Energy lost by building ventilation( (this factor is required to be considered from insulation specification 1995)
Qs: Solar thermal energy obtained;
Qi: Indoor heat energy;
Qt,d: Heat loss of roof;
Qt,aw: Heat loss of exterior wall;
Qt,f: Heat loss of windows;
Qt,b: Heat loss of floor;
QT: Equipment heat loss( (calculation is required from the energy saving specification 2002)
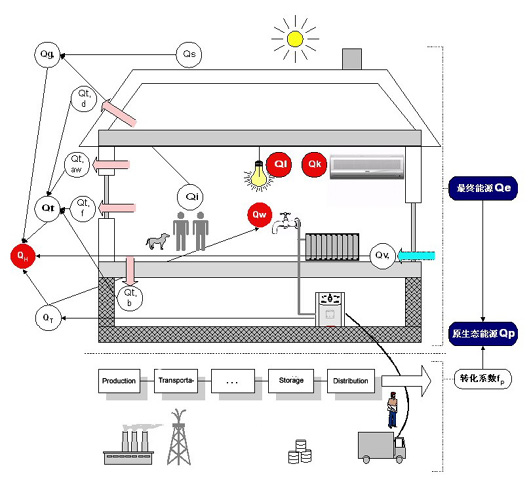
Definition of building energy consumption in the energy conservation specification
In addition to the standard calculation method, the simplified calculation method can also be adopted if certain conditions are met.
The specific calculation formula is continued in Chapter V, the calculation of building energy demand.
IV Norms or specification of energy conservation and requirements for gradually improve energy conservation
The building energy conservation specification in Germany is revised every two or three years, and the requirements for energy conservation are gradually improved. The following table shows the comparison of thermal conductivity of building envelope components and heating energy demand of buildings.
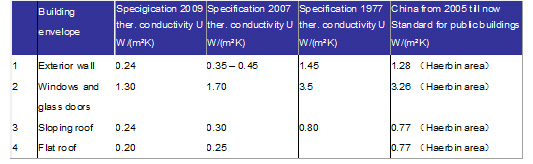
Comparison of thermal conductivity of building envelope
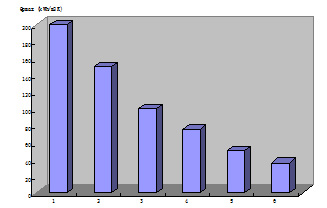
Comparison of building heating energy demand
We should see that it is not difficult to make requests for whatever, but if we can't meet the requirements, we are just drawing cakes to satisfy our hunger. It is not easy for the the building energy efficiency specification of Germany to gradually improve the energy-saving requirements step by step, which leads to the creation of a series of green and energy-saving new building materials and the innovation of building technology, the promotion of the use of renewable energy, the pursuit of improving the efficiency of building equipment, the exploration of improving building shape design, construction structure and construction technology, and so on. The following are the key points of modification of Energy Conservation Specification 2007 in energy conservation specification 2009, from which we can learn:
It improves the energy-saving requirements for new and reconstructed old buildings
The maximum annual original ecological energy demand of new buildings is reduced by 30%;
The thermal insulation requirements of new buildings are increased by 15%;
The energy-saving requirements for major improvements of old buildings (such as the reconstruction of roof, outer wall and windows) shall be increased by 30%;
After the renovation of old buildings, the annual demand for original ecological energy must be reduced by 30%, and the thermal insulation requirements must be increased by 15%;
The requirements for energy-saving of the old building envelope are improved
Calculation according to DIN V 18599 or DIN V 4108-6 and DIN V 4701-10;
The coefficient used in estimating the original ecological energy demand from power consumption is reduced from 2.7 to 2.6;
Encourage the use of green electricity
In the following cases, the electric energy generated by renewable energy shall be deducted when calculating the final energy material demand:
Generation of renewable energy directly related to buildings;
It is firstly used for the building itself, and the surplus is fed into the public power netting;
Gradually abolish the old provisions on electric heating equipment
By the end of 2008, all heating equipment using oil or gas manufactured before 1978 had been abolished. On this basis, by December 31, 2019, except under special circumstances, electric heating equipment (excluding floor heating equipment) that has been used for more than 30 years must be abolished;
Provisions for improving the implementation of specifications
Contact professionals to inspect the heating facilities and confirm that the old heaters that do not meet the specification requirements are no longer in use;
The enterprise shall declare that the old buildings and their equipment and devices used have been reconstructed to meet the specification requirements;
The enterprise has the obligation to show the statement to the official responsible organization, otherwise it will be punished as violating the norms;
Formulate violation handling measures for intentional and minor violations on energy conservation norms for the cnstruction of new buildings and the reconstruction of old buildings, or the use of incorrect data in make of the building energy consumption certificates.
Notes: BEE is the abbreviation for Building Energy Efficiency.